Short-lived detection of eDNA
Environmental DNA (eDNA) is increasingly used to measure biodiversity of marine ecosystems, yet key aspects of the temporal dynamics of eDNA remain unknown. Of particular interest is in situ persistence of eDNA signals in dynamic marine environments, as eDNA degradation rates have predominantly been quantified through mesocosm studies. For my undergraduate senior honors thesis project, I investigated in situ eDNA residence times. We introduced an eDNA signal from a non-native fish into a protected bay of a Southern California rocky reef ecosystem, and then measured changes in both introduced and background eDNA signals across a fixed transect over 96 hours.
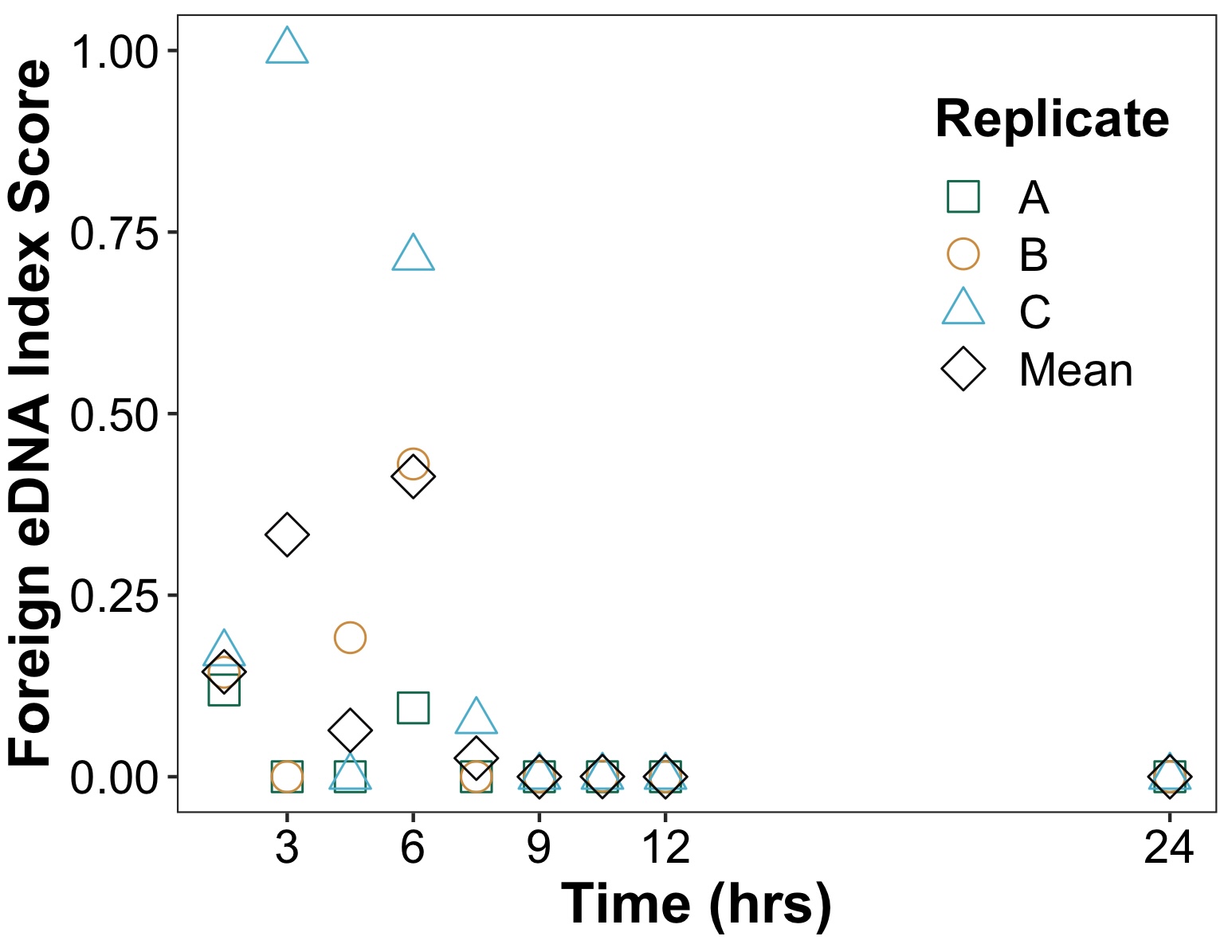
Foreign eDNA signal was no longer detected only 7.5 hours after introduction, a time substantially shorter than the multi-day persistence times in laboratory studies. Moreover, the foreign eDNA signal spread along the entire 38 m transect within 1.5 hours after introduction, indicating that transport and diffusion play a role in eDNA detectability even in protected low energy marine environments.
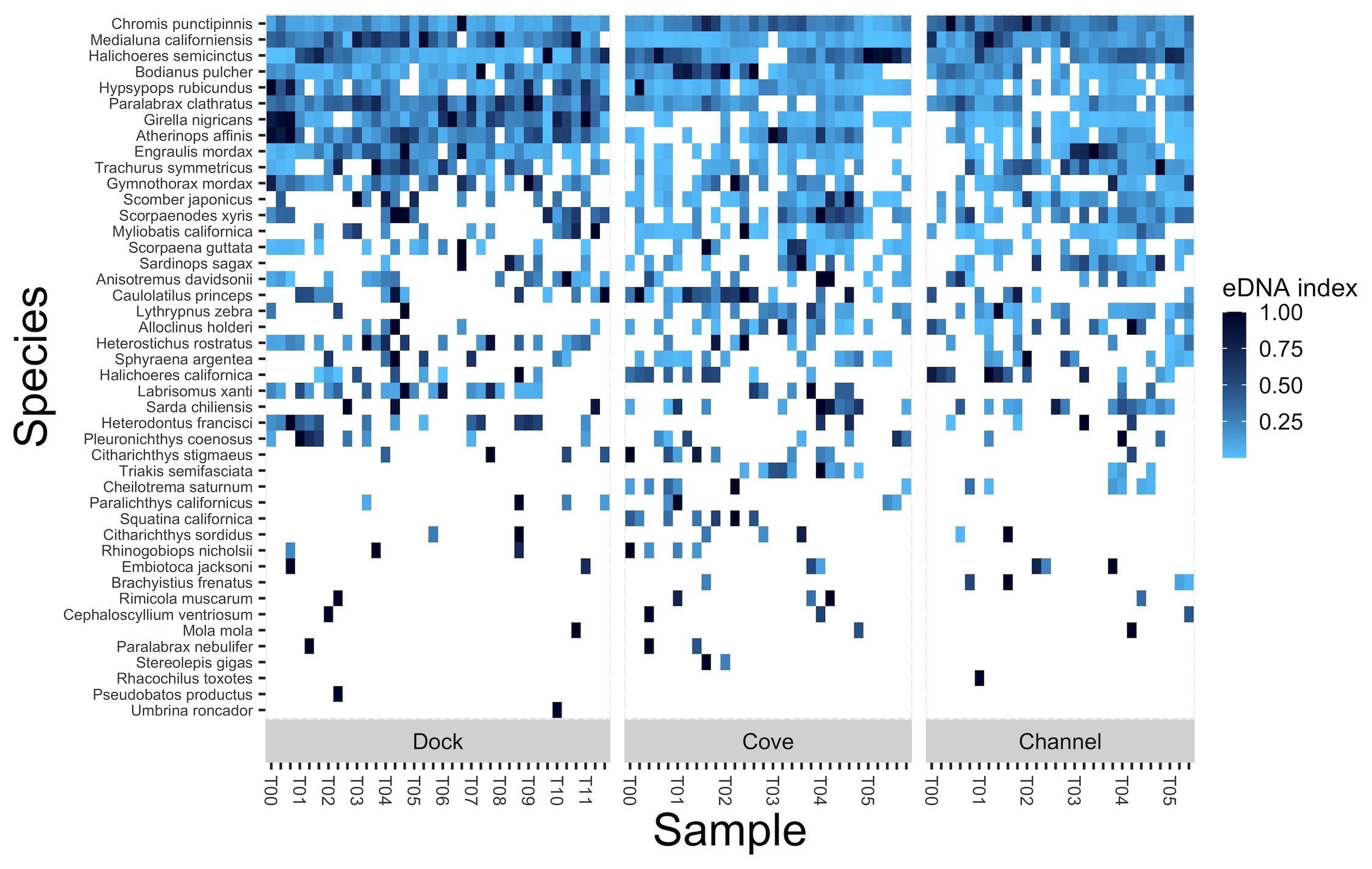
Similarly, native vertebrate eDNA signals varied greatly over the 96 hours of observation as well as within two additional nearby fixed transects sampled over 120 hours. While community structure did significantly change across time of day and tidal direction, neither accounted for the majority of observed variation. Combined, results show that both foreign and native eDNA signatures can exhibit substantial temporal heterogeneity, even on hourly time scales. Further work exploring eDNA decay from lagrangian perspective and quantifying effects of sample and technical replication are needed to better understand temporal variation of eDNA signatures in nearshore marine environments.
I presented my senior honors thesis at both the UCLA Research Poster Day and UCLA Annual Biology Research Symposium where I was awarded third place for undergraduate posters.
Published paper is open access here